Solar Thruster Sailor (STS) - Fig´s (Fig 8 - 8 b)
- © Frank Ellinghaus -
Fig.1 -
Fig.2a-2b -
Fig.2c -
Fig.2d -
Fig.3a-3b -
Fig.4a-4c -
Fig.5 -
Fig.6 -
Fig.7 -
Inner Ring -
Flying Ring -
Fig.8 -
Fig.8a -
Fig.8b -
Fig.9 -
Fig.9a -
Fig.10 -
Fig.11 -
Fig.10 -
Fig.11 -
Fig.13 -
Fig.14-15 -
Fig.16 Mobile Thruster Unit -
Fig.17 -
Fig.18 Fuelless Steering -
Fig.19-21d Solar Sail Launch System
Figures 8 - 8b - The Inner Ring as a Docking- and Loading- Station for Thruster-Ring-Spacecrafts and Solar Sails - N E W
Thruster Ring Space Crafts as show´n in Fig. 1 have the advantage to provide a large area for payload storage. What lacks is the possibility to handle, fasten and store payload automaticly. The Inner Ring does just that. It has devices attached (electric winches or automatic docking brackets) which enable payload handling or give smaller Thruster Ring Space Crafts the ability to dock in and cast off at a carrier ship.
The Inner Ring is attached to the center of the Outer Ring of the space craft with belts, tethers or thread - preferably made of strong and lightweight nanotube like materials. The carrier holds the payload in the free space area of the Inner Ring construction.
There are different Inner Ring construction possibilities, from the bare one ring single loading and docking station ( fig. 8 ) to the double station ( fig. 8a ) (for up- and downside docking and handling) and at least to the magazine station ( fig. 8.b ) which makes it possible to transport swarms of satellites, space crafts, landers or container units.
Figure 8 - Inner Ring construction as 1-Slot Docking- and Loading Station for a Thruster Ring Spacecraft
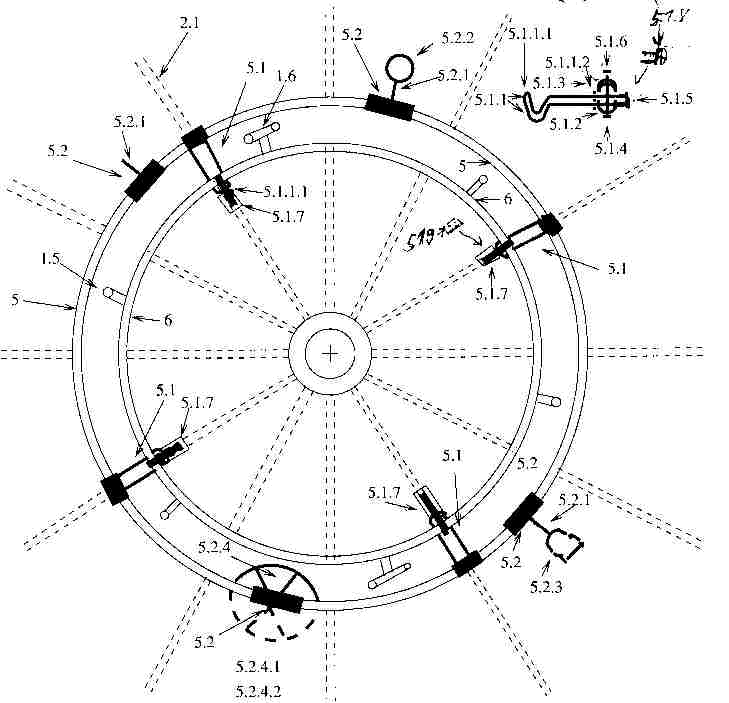 Figure 8 shows a simple one slot loading and docking station which consists of the Inner Ring 5 with devices for docking and loading attached to it. The outer ring of the carrier ship is not shown here, simply because of the size difference of the thruster ring which would be huge in comparisation to the Inner Ring.
Figure 8 shows a simple one slot loading and docking station which consists of the Inner Ring 5 with devices for docking and loading attached to it. The outer ring of the carrier ship is not shown here, simply because of the size difference of the thruster ring which would be huge in comparisation to the Inner Ring.
There are 4 docking brackets 5.1 attached to the Inner Ring 5 which hold in this case a smaller Thruster Ring Spacecraft at it´s Outer Thruster Ring 6. The picture shows also 4 electric winches 5.2 on the docking station with 4 different devices attached to it. This is only thought to show some of the different possibilities for payload handling. In reality there would be more than one devices of one type to handle the payload and hold it tight with the winches.
In this case the devices are
- 5.2.1 - a simple thread or belt to fix payload with a knot.
- 5.2.2 - thread or belt with a ring
- 5.2.3 - thread or belt with a carabiner hook
- 5.2.4 - thread or belt with a flying ring
The Flying Ring is just a little thruster ring space craft. In this case it is thought as the end part of electric winches equipped with devices as mentioned above which enable it to handle objects. The object would just being grabbed by several of this flying rings and held taught with the help of the winches. So this Thruster Ring Spacecraft with an Inner Ring would be able to handle payload by remote.
Figure 8. a
Figure 8. a shows a double docking and loading slot.
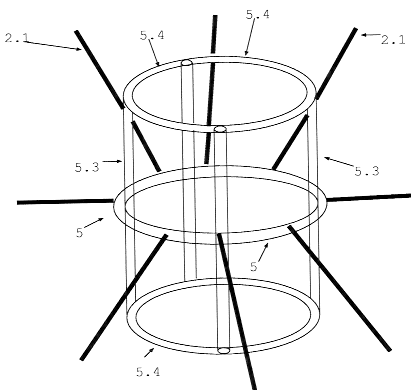
This double Docking and Loading Station allows docking and handling at the same time from both, upside and downside. For instance an explorer spacecraft has a lander docking in or out at the upper side and at the same time an object at an asteroid is handled with the winch devices underside the explorer.
The drawing shows just the bare pipe sceleton. The double slot is held by belts at it´s middle ring 5. As in figure 8 it is possible to rig the rings on both sides with brackets and handling devices.
Figure 8. b - Magazine Docking Station
Figure 8. b shows a magazine docking and loading slot for spacecraft swarms or fleets or for flying containers.
 The swarm spacecrafts can move into and out of the tubular free space inside the ring constuction. They will be held through moveable electric brackets which extract into the docking space.
The swarm spacecrafts can move into and out of the tubular free space inside the ring constuction. They will be held through moveable electric brackets which extract into the docking space.
At the drawing we see one daughter unit held in one slot short above the middle ring which is held by belts and leashes to the outer ring of the carrier ship. Spacecraft or satellite swarms could be carried with such a device.
The carrier could also serve as container ship were the containers are free flying spacecrafts which are able to dock in and out with their own electric thrusters.
to the next Fig. 9 - not yet
Fig.1 -
Fig.2a-2b -
Fig.2c -
Fig.2d -
Fig.3a-3b -
Fig.4a-4c -
Fig.5 -
Fig.6 -
Fig.7 -
Inner Ring -
Flying Ring -
Fig.8 -
Fig.8a -
Fig.8b -
Fig.9 -
Fig.9a -
Fig.10 -
Fig.11 -
Fig.10 -
Fig.11 -
Fig.13 -
Fig.14-15 -
Fig.16 Mobile Thruster Unit -
Fig.17 -
Fig.18 Fuelless Steering -
Fig.19-21d Solar Sail Launch System



